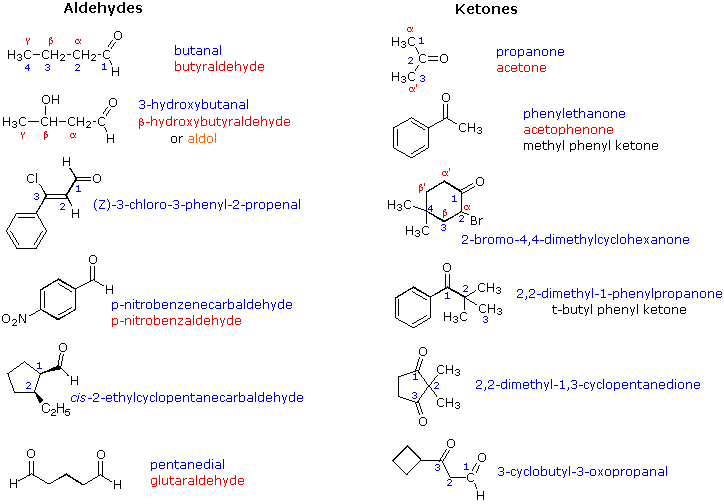
Ketone:
- they are carbon compounds
- they have a double bonded oxygen
- has the ending of -one
- the double bond can't be in the beginning or end
- the double bond has to be the lowest number possible
Aldehydes:
- double bonded oxygen
- at either the begging or ending of the parent chain
Alcohols:
- OH (hydroxyl)
- number of Carbons (meth,eth, etc...)
- has the ending of -nol
- phenol is an exception
- has an OH bonded to it
- numbering says where OH is
- more than one OH, add -diol, triol etc...
 |
| Ex: methanol |
Halides:
- they contain halogens from group 17 (Bromine, Chlorine, Iodine, Fluorine
- the halogens have the ending of -o
- the numbers show where the halogens are

1 Chloroethane

1,2 dichloroethane
Ethers:
- have an ending of -er
- only contains oxygen
- always between 2 carbons
- not in alphabetical order, it's in numerical order
- starts with methyl

Amines:
- has the ending of -yl amine
- nitrogen is placed between each carbon

Amides:
- ends in -anamide
- has a double bonded oxygen and NH2

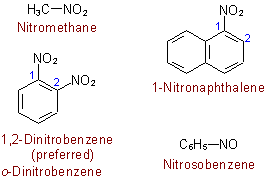
Nitros:
- starts with nitro-
- has a nitrogen with a double bonded oxygen
- has a single bond oxygen
Esters:
- there is an Oxygen in the parent chain
- double bonded O in side chain
- parent chain ends in -oate
- side chain and "O" sandwich a carbon

Carboxylic Acids:
- use the standard rules but change the parent chain ending to -oic acid
-has a double bonded O and an OH bonded to the first carbon
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AYtXm7NizQA&feature=related
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C5ZK6nPPAbo&feature=related
By: KRYSTA DEL ROSARIO